One more post, you will see something about databases, springboot, java, xml, h2, flyway for h2 to postgreSQL migration, securize a little bit in postgreSQL and that’s it, more of the same.
Migrating Script de h2 to PostgreSQL
|
Migration
|
Properties for h2
### spring config
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:db (1)
username: test
password: test| 1 | db: is the name of our database. |
Dependencies for our pom.xml
I’m already with a spring parent and therefore the version inherits it, that’s why the <version> tag is not present.
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.3.6</version>
</parent><dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
In this springboot version 3.3.6 the h2 console must be enabled in our security, to be able to access it at least in development.
|
@Bean
public WebSecurityCustomizer ignoringCustomizer() {
return (web) -> web.ignoring().requestMatchers("/h2-console/**");
}From the UI when we connect we can do this
|
Tips
|
SCRIPT TO 'dump.sql' (1)| 1 | This will create a file named dump.sql inside the project directory, no need to copy and paste 😚 |
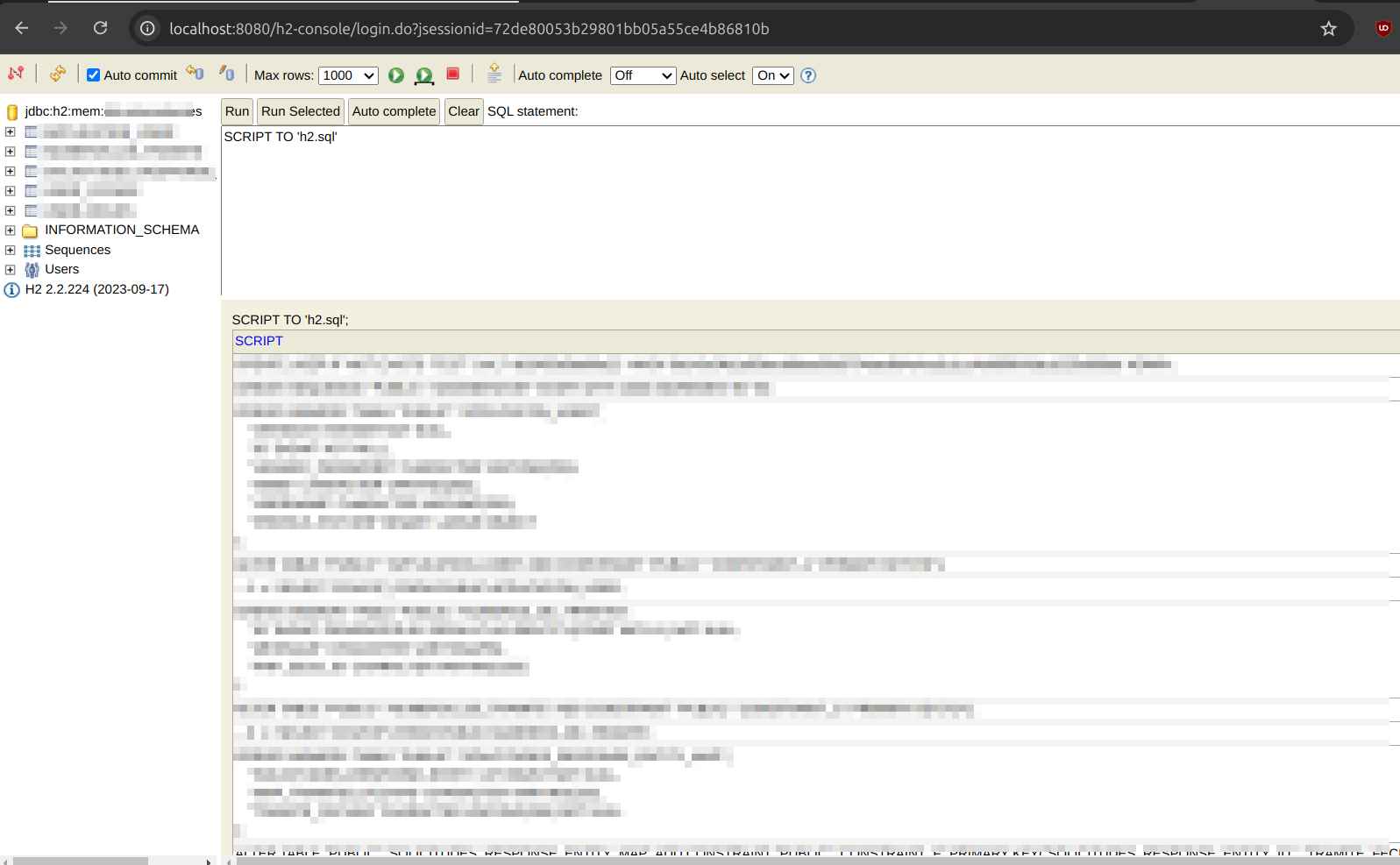
|
Renamed
|
The docker compose file
We need to have postgresql up at least locally, or use testcontainer.
services:
postgres:
image: 'postgres:latest'
environment:
- 'POSTGRES_DB=mydatabase'
- 'POSTGRES_PASSWORD=secret'
- 'POSTGRES_USER=myuser'
ports:
- '5432:5432'Reconfiguring Springboot properties
Flyway must take care of the database structure, so it is important to disable Hibernate’s auto-creation.
### spring config
spring:
jpa:
defer-datasource-initialization: true
show-sql: true
generate-ddl: false (1)
hibernate
ddl-auto: none (2)
properties:
hibernate:
format_sql: true
#Config Flyway
flyway:
enabled: true
baseline-on-migrate: true
out-of-order: true
datasource:
url: jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydatabase
username: myuser
password: secret
driverClassName: org.postgresql.Driver (3)| 1 | deactivated. |
| 2 | deactivated. |
| 3 | This property is supposed to be optional. |
This prevents Hibernate from trying to modify the database before Flyway does its work.
Updating the pom.xml
With these postgresql and flyway driver dependencies
<!--<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId> (1)
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency> -->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.flywaydb/flyway-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-core</artifactId>
<version>11.3.0</version> (2)
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.flywaydb</groupId>
<artifactId>flyway-database-postgresql</artifactId> (3)
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresql</groupId>
<artifactId>postgresql</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>| 1 | Commented h2 dependency. |
| 2 | Important to have it to avoid errors like Caused by: org.flywaydb.core.api.FlywayException: Unsupported Database: PostgreSQL 17.2. |
| 3 | Also important. |
Possible error at startup, with jpa and flyway
org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'entityManagerFactory' defined in class path resource [org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/orm/jpa/HibernateJpaConfiguration.class]: Failed to initialize dependency 'flyway' of LoadTimeWeaverAware bean 'entityManagerFactory': Error creating bean with name 'flyway' defined in class path resource [org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/flyway/FlywayAutoConfiguration$FlywayConfiguration.class]: Circular depends-on relationship between 'flyway' and 'entityManagerFactory'Most probably we have postponed the initialization of the Datasource in our properties file, we must have it like this, with false:
-
defer-datasource-initialization: false
Case with existing db and data
The configuration when we have existing data in the db, and we do not want to touch any of our data, we must change the properties for example:
flyway:
schema: our-schema
baseline-on-migrate: true
baseline-version: 0
clean-disabled: true
validate-on-migrate: falseAlso create a file, in db.migration for example: V1.1__baseline.sql with this:
-- Baseline migration - existing structureWhen we start flyway it will version this script, in the public schema of our db.
SELECT * FROM flyway_schema_history;installed_rank|version|description|type|script |checksum |installed_by|installed_on |execution_time|success|
--------------+-------+-----------+----+------------------+----------+------------+-----------------------+--------------+-------+
1|1.1 |baseline |SQL |V1.1__baseline.sql|-385248959|admin |fecha | 6|true |For the future we can create new migrations following the Flyway naming convention:
V1.2__descripcion.sql
V1.3__descripcion.sql|
We should be careful with this:
|
Some IDE configurations
If we update the user’s .bashrc file with environment variables, we must restart the IDE so that the variables are refreshed correctly, otherwise they will point to incorrect versions.
|
Local spring profile
If we have several profiles we must be attentive to load the correct profile, local I some other.
-
For local from the IDE, we can use
--spring.profiles.active=localhere:
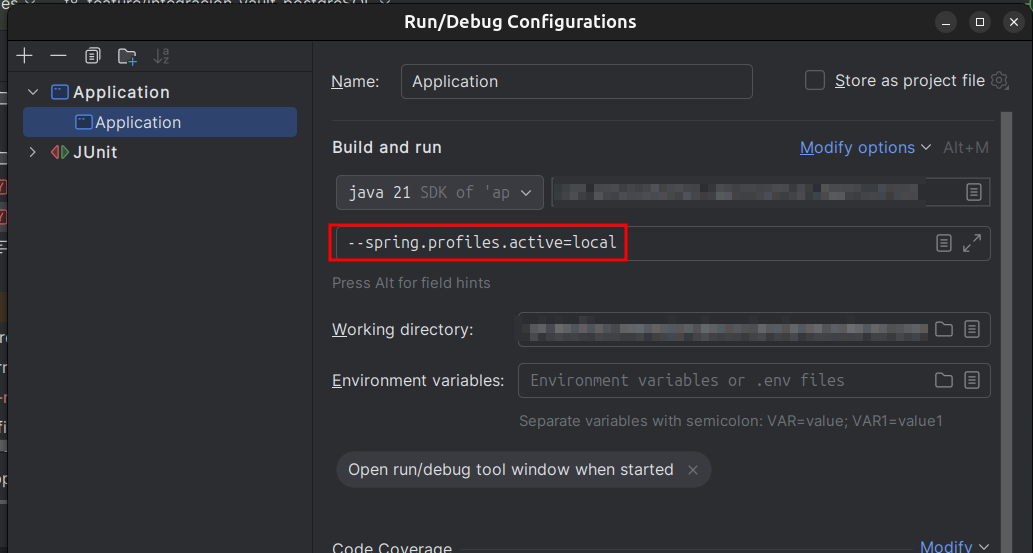
Therefore, in the console we should see the following:
2025-02-10T20:30:14.347+01:00 INFO 1228306 --- [ restartedMain] c.x.x.Application : The following 1 profile is active: "local" (1)| 1 | The local profile, application-local.yml loaded correctly. |
Successfully loading the IDE .bashrc
It is important to make sure that our ide loads the .bashrc correctly where we have the environment variables set as in the image, it is very useful.
/bin/bash --login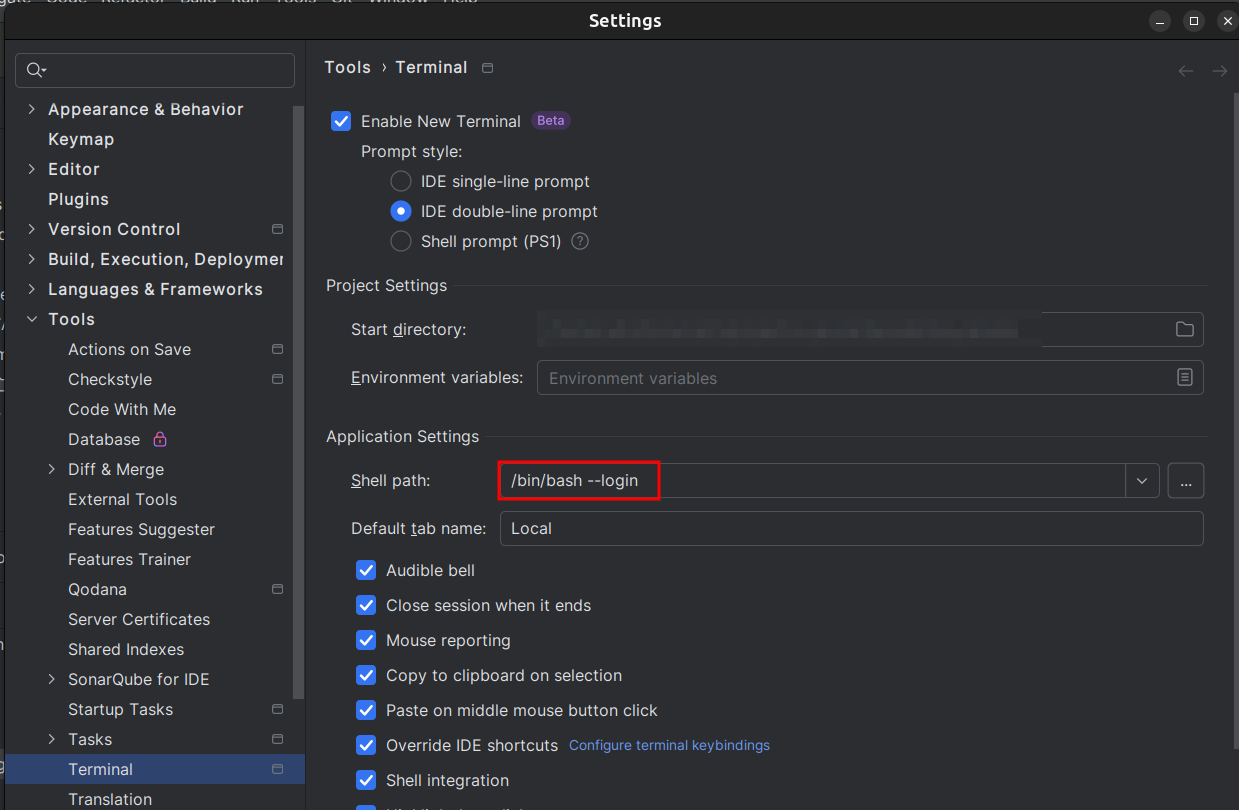
/home/rubn/.local/share/applications/IntelliJ.desktop#!/usr/bin/env xdg-open
[Desktop Entry]
Type=Application
Name=IntelliJ
StartupWMClass=jetbrains-idea-ce
Exec=/bin/bash -i -c "/home/rubn/Downloads/jdk-ide/idea/bin/idea" %f (1)
Icon=/home/rubn/Downloads/jdk-ide/idea/bin/idea.svg
Categories=Network;Application;| 1 | Here we force the interactive mode loading with the -i parameter |
Every change in this file requires a restart with source .bashrc or the file where we have these properties.
Instaling PostgreSQL FreeBSD
The wiki in our friend PostgreSQL/Setup
| A bit of postgres with springboot for security |
Security is usually important, we always use for the test the postgres version 15, for them we quickly enable a jail with bastille using the template for example this one
Applying it to the existing jail called postgresql
bastille template TARGET yaazkal/bastille-postgres (1)| 1 | TARGET is the name of our jail |
Only with localhost access localhost
Yes, I have just enabled to use psql from the server itself with this line in the pg_hba.conf file
# "local" is for Unix domain socket connections only
local all all trust (1)| 1 | The other lines for recommendation better be with scram-sha-256 for trust or MD5 |
Migrating passwords to SCRAM
| Review this |
The postgresql.conf file needs to be updated with the following line
# - Authentication -
#authentication_timeout = 1min # 1s-600s
password_encryption = scram-sha-256 # scram-sha-256 or md5 (1)| 1 | Here you can uncomment and use scram-sha-256 |
postgres=#
SELECT rolname, rolpassword ~ '^SCRAM-SHA-256\$' AS has_upgraded
FROM pg_authid
WHERE rolcanlogin; rolname | has_upgraded
----------+--------------
postgres |
admin | t (1)
(2 rows)| 1 | Indicates true, which is already updated |
It is possible that in order to authenticate from our java client with spring you may have some problems such as
Caused by: org.postgresql.util.PSQLException: FATAL: password authentication failed for user "admin"Recommended upgrade
$ psql
psql (14.15)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# \password admin (1)
Enter new password for user "admin":| 1 | Using password the correct update of the passwords is done. 🔥 |
ALTER ROLE admin WITH PASSWORD 'pass'; (1)| 1 | This is not recommended for the update, besides leaving a trace in the history. |
To restart db
service postgresql reloadThe command \du
Allows us to see the roles with their attributes
postgres=# \du
List of roles
Role name | Attributes | Member of
-----------+------------------------------------------------------------+-----------
admin | Create DB | {}
postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {}Importing schemas
To do this we can use the command
psql -U \ (1)
admin -d \ (2)
ott -a -f /var/db/postgres/ott-schema.sql (3)| 1 | PostgreSQL in interactive mode, with the -U user parameter. |
| 2 | The -d command for the ott database. |
| 3 | The -a command prints all the lines, and -f is the path where the postgres user has read permissions, needed to import the .sql. |
Encoding for password
If we use by default the JdbcUserDetailsManager bean for the InMemoryUserDetailsManager bean, we will use the JdbcUserDetailsManager bean for the InMemoryUserDetailsManager bean.
@Bean
public JdbcUserDetailsManager jdbcUserDetailsManager(DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcUserDetailsManager(dataSource);
}We must add a default encoder at least
java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Given that there is no default password encoder configured, each password must have a password encoding prefix. Please either prefix this password with '{noop}' or set a default password encoder in `DelegatingPasswordEncoder`.In the default hash of spring security is a SHA-256
username|password |enabled|
--------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
boby |843b103f6c09de407d366f8ff6553691767a35dbaf870cad47e86945c4103be85ee8ea49509b9502|true |
chispa |a94f80ed1a6677dedb489a6912e6c83a7c2a7ada2c4d739dd4a4ab9e454d3d875134fa4480b19c55|true |We update by adding a hash template
UPDATE users SET password = '{sha256}' || password;username|password |enabled|
--------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
boby |{sha256}843b103f6c09de407d366f8ff6553691767a35dbaf870cad47e86945c4103be85ee8ea49509b9502|true |
chispa |{sha256}a94f80ed1a6677dedb489a6912e6c83a7c2a7ada2c4d739dd4a4ab9e454d3d875134fa4480b19c55|true |If we apply this other bean and log into the spring security login the password encoder will be changed to bcrypt in the background.
@Bean
public UserDetailsPasswordService userDetailsPasswordService(UserDetailsManager userDetailsManager) {
return (user, newPassword) -> {
var updated = User.withUserDetails(user)
.password(newPassword)
.build();
userDetailsManager.updateUser(updated);
return updated;
};
}Migration under background to bcrypt.
username|password |enabled|
--------+----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+-------+
boby |{sha256}843b103f6c09de407d366f8ff6553691767a35dbaf870cad47e86945c4103be85ee8ea49509b9502|true |
chispa |{bcrypt}$2a$10$dMqSFw875ZLvpsADb24XDezNMacIYqC4bIUkbb24QOLYE3pmlZInS |true |Already that bcrypt tells us that it was a successful update.
Integration with hashicorp
Although the encoding with bcrypt is interesting, let’s delegate the secrets better in the vault, and not in postgres.
Secrets from the vault with TLS
As we have already configured our vault with SSL/TLS we can bring the secrets using certificate to authenticate us.
At the moment when trying to do it from spring we have the following, in our property file
### spring config
spring:
### Vault
config:
import: vault://
cloud:
vault:
uri: ${URL_VAULT} (1)
token: ${INITIAL_ROOT_TOKEN} (2)
kv:
enabled: true
backend: app
application-name: nombre-app
ssl:
key-store: classpath:/cert/vault-cert.p12 # O file:/ruta/completa/mi-certificado.p12
key-store-password: pass # La passphrase de nuestro certificado
key-store-type: PKCS12| 1 | Url of the vault, in https |
| 2 | The initial root token |
org.springframework.vault.VaultException: Status 400 Bad Request [path/secreto]: Client sent an HTTP request to an HTTPS server. (1)| 1 | Attempt to connect secrets via normal http, without certificate, the server rejects us when bringing us the secrets. |
As we already have our customer certificate .p12 we must use it to authenticate for example with keytool to import the ca:
keytool -import -trustcacerts -alias vault-ca -file ca-cert.crt -keystore vault-truststore.jks
...
...
Trust this certificate? [no]: yes (1)
Certificate was added to keystore| 1 | We write yes |
We should have generated the vault-truststore.jks then, now to test the connection
Now we add trust-store properties to the src/main/resources/cert for quick testing.
|
FYI Sobre file
|
ssl:
(1)
key-store: file:src/main/resources/cert/vault-cert.p12 # O file:/ruta/completa/mi-certificado.p12
key-store-password: pass # The passphrase of our certificate
key-store-type: PKCS12
# Trust store to validate the server certificate
trust-store: file:src/main/resources/cert/vault-truststore.jks
trust-store-password: pass (2)
trust-store-type: JKS| 1 | For the sake of brevity and safety we will use file, also this classpath when we will use the final .jar of PROD. |
| 2 | The password entered when executing the keytool command. |
Vault is sealed
When the vault is sealed we have this error, a 503, we must first remove the seal to be able to work with it, which is happening by a complete restart of the server in our case, clearly with the 3 keys of the 5 available we have…
Caused by: org.springframework.vault.VaultException: Status 503 Service Unavailable [antecedentes]: Vault is sealed (1)
at org.springframework.vault.client.VaultResponses.buildException(VaultResponses.java:84) ~[spring-vault-core-3.1.2.jar:3.1.2]
at org.springframework.vault.core.VaultKeyValueAccessor.lambda$doRead$2(VaultKeyValueAccessor.java:174) ~[spring-vault-core-3.1.2.jar:3.1.2]
at org.springframework.vault.core.VaultTemplate.doWithSession(VaultTemplate.java:451) ~[spring-vault-core-3.1.2.jar:3.1.2]
at org.springframework.vault.core.VaultKeyValueAccessor.doRead(VaultKeyValueAccessor.java:163) ~[spring-vault-core-3.1.2.jar:3.1.2]
at org.springframework.vault.core.VaultKeyValueAccessor.doRead(VaultKeyValueAccessor.java:132) ~[spring-vault-core-3.1.2.jar:3.1.2]
at org.springframework.vault.core.VaultKeyValueAccessor.doRead(VaultKeyValueAccessor.java:107) ~[spring-vault-core-3.1.2.jar:3.1.2]
at org.springframework.vault.core.VaultKeyValue2Template.get(VaultKeyValue2Template.java:56) ~[spring-vault-core-3.1.2.jar:3.1.2]| 1 | Vault with seal. |
The spring configuration for mapping of secrets
We already have the secrets available in our vault, now we can map them to our Java object, via @ConfigurationProperties.
| Explicitly in the vault, I have a secret followed by a dot . to use it with the spring bean to make mapping easier. |
@Data
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties("secret") (1)
public class SecretsConfiguration {
private String chispita;
}| 1 | Indicating that, in the vault would be secret.chispita with the value of the secret. |

